Living with diabetes can be challenging, but adopting a Low Carb Diabetes Diet provides an effective way to manage blood sugar and improve overall health. At Deepa Hospital, we prioritize tailored dietary approaches to help patients regain control over their condition. By reducing carbohydrate intake and focusing on balanced nutrition, individuals with diabetes can experience sustainable improvements in their quality of life.
What is a Low Carb Diabetes Diet?
A Low Carb Diabetes Diet reduces carbohydrate consumption while emphasizing proteins, healthy fats, and nutrient-dense vegetables. It is particularly beneficial for individuals with Type 2 diabetes. Many of our patients at Deepa Hospital have witnessed transformative health benefits after adopting this approach.
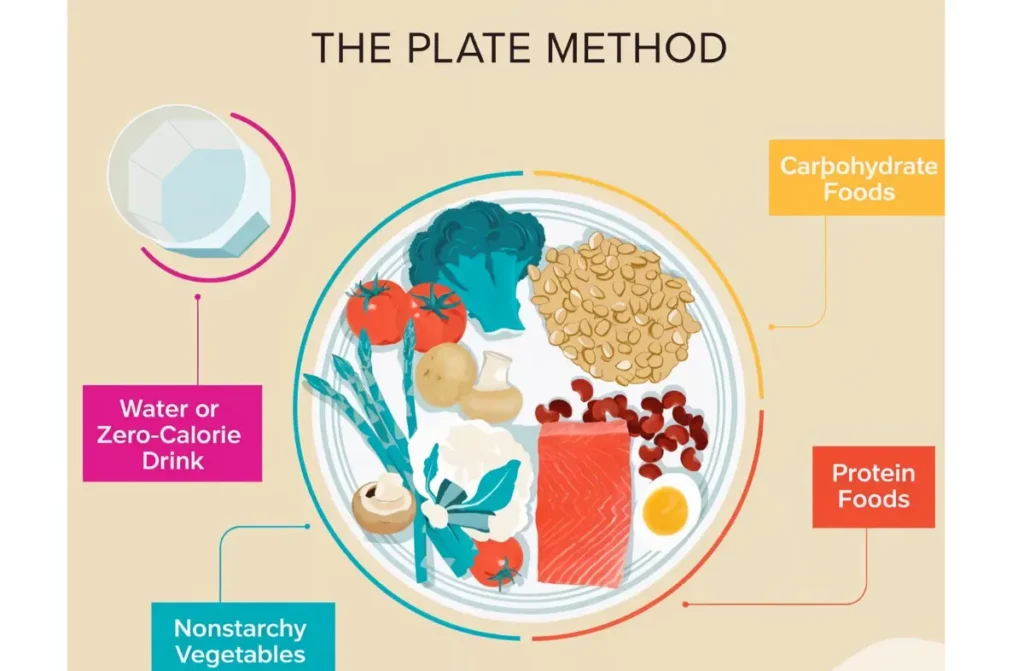
Key Features of a Low Carb Diabetes Diet:
- Balanced Nutrients: Replace high-carb foods with lean proteins (e.g., grilled chicken), healthy fats (e.g., avocado), and fiber-rich vegetables (e.g., spinach).
- Reduced Processed Foods: Avoid sugary drinks, refined grains, and packaged snacks, which lead to blood sugar spikes.
- Sustainable Lifestyle Changes: The diet focuses on informed choices rather than deprivation, ensuring long-term adherence.
Low Carb Diabetes Diet List
A Low Carb Diabetes Diet helps manage blood sugar levels effectively while providing essential nutrients. Below is a table outlining low-carb food options:
| Food Category | Best Low-Carb Options | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetables | Spinach, Broccoli, Cauliflower, Zucchini | High in fiber, low in carbs |
| Fruits | Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries) | Low sugar, rich in antioxidants |
| Proteins | Chicken, Fish, Eggs, Tofu | Supports muscle health, stabilizes blood sugar |
| Dairy | Greek Yogurt, Cheese, Cottage Cheese | Provides calcium and protein |
| Nuts & Seeds | Almonds, Walnuts, Chia Seeds, Flaxseeds | Healthy fats, good for heart health |
| Healthy Fats | Olive Oil, Avocados, Coconut Oil | Supports brain and heart function |
| Whole Grains | Quinoa, Flaxseed, Chia Seeds | Provides fiber and sustains energy levels |
Is a Low Carb Diabetes Diet Right for You?
A Low Carb Diabetes Diet can help control blood sugar and reduce insulin resistance. However, it’s important to consult a doctor before making dietary changes.
How Does a Low Carb Diabetes Diet Work
The primary mechanism of a Low Carb Diabetes Diet is reducing carbohydrate intake, which shifts the body’s metabolism from using glucose as the primary energy source to burning fat. This process, known as ketosis, helps stabilize blood sugar levels, reduce insulin resistance, and promote weight loss.
For those on a Low Carbohydrate Diet for Type 2 Diabetes, this dietary shift often results in:
- Lower blood sugar fluctuations.
- Reduced dependency on medication.
- Long-term improvement in A1C levels.
The Role of Carbohydrates in Diabetes Management
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source. However, consuming excessive carbs can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, especially for individuals with diabetes. Understanding How Many Carbs Should a Person with Diabetes Have? is critical for effective management.
Why Carbs Matter:
- Simple Carbs: Found in sugary drinks, candies, and white bread, these are digested quickly, causing blood sugar spikes.
- Complex Carbs: Found in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, these digest slowly, leading to a steady rise in blood sugar.
At Deepa Hospital, we guide patients in balancing their carb intake, emphasizing good carbs while minimizing bad carbs for optimal diabetes management.
Benefits of a Low Carbohydrate Diet for Type 2 Diabetes
For individuals with Type 2 diabetes, a Low Carbohydrate Diet for Type 2 Diabetes offers numerous benefits:
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: Reducing carb intake prevents sudden sugar spikes.
- Enhanced Insulin Sensitivity: Helps the body respond better to insulin.
- Weight Management: Aids in reducing visceral fat, which is strongly linked to diabetes.
- Reduction in Medications: Many patients on a Low Carbohydrate Diet for Type 2 Diabetes report needing less medication.
Deepa Hospital ensures every patient receives personalized dietary advice to maximize these benefits.
Understanding Carb Intake: How Many Carbs Should a Person with Diabetes Have?
The ideal carbohydrate intake varies based on factors such as age, activity level, and the severity of diabetes. At Deepa Hospital, we provide tailored recommendations to ensure sustainable success.
Guidelines for Carb Intake:
- Start Gradually: Begin by reducing your carb intake to allow the body to adapt.
- Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods: Incorporate leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and non-starchy vegetables.
- Monitor Regularly: Keep track of your blood sugar levels to refine your carb intake.
For many patients, a Low Carbohydrate Diet for Type 2 Diabetes consisting of 20-50 grams of carbs per day proves effective.
What Is The Best Low Carb Diet For Diabetics?
The best low-carb diet for diabetes is one that prioritizes whole, unprocessed foods while minimizing simple carbs. At Deepa Hospital, we help patients explore What Is The Best Low Carb Diet For Diabetics? based on their preferences and lifestyle.
Key Components of an Ideal Low Carb Diet:
- High-Quality Proteins: Lean meats, fish, and plant-based options like tofu.
- Healthy Fats: Avocado, olive oil, and nuts.
- Low-Glycemic Vegetables: Broccoli, spinach, and zucchini.
By choosing foods that have minimal impact on blood sugar, patients can achieve better glucose control and overall health.
How Carbohydrates Affect Blood Sugar
Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which directly impacts blood sugar levels. Simple carbs cause quick spikes, whereas complex carbs lead to steadier glucose release.
Why It’s Important:
- Simple Carbs to Avoid: Sugary drinks, refined grains, and processed snacks.
- Complex Carbs to Include: Whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables in moderation.
Understanding How Many Carbs Should a Person with Diabetes Have? enables individuals to make better food choices, balancing energy needs with blood sugar management.
Can a Very Low Carb Diabetes Diet Reverse Type 2 Diabetes?
For many patients, a very Low Carb Diabetes Diet can significantly improve or even reverse Type 2 diabetes symptoms. At Deepa Hospital, we have seen patients experience:
- Better A1C levels.
- Improved insulin sensitivity.
- Reduced reliance on medications.
By understanding What Is The Best Low Carb Diet For Diabetics?, patients can take charge of their health with confidence.
Foods to Avoid and Embrace on a Low Carb Diabetes Diet
High-Carb Foods to Avoid:
- Sugary Beverages: Soda, fruit juices, and sweetened teas.
- Refined Grains: White bread, pasta, and rice.
- Sweet Snacks: Cookies, cakes, and candies.
Healthier Alternatives:
- Zucchini Noodles: A low-carb pasta substitute.
- Cauliflower Rice: A nutritious replacement for white rice.
- Unsweetened Beverages: Herbal teas and water.
What Is The Best Low Carb Diet For Diabetics?
The best diet varies, but it generally includes:
- Low-Glycemic Vegetables: Broccoli, spinach, and kale.
- High-Protein Foods: Eggs, poultry, and fish.
- Healthy Fats: Avocado, olive oil, and seeds.
By addressing How Many Carbs Should a Person with Diabetes Have?, patients can personalize their meal plans effectively.
The Role of Protein and Fats in Diabetes Management
In a Low Carb Diabetes Diet, proteins and fats play a crucial role:
- Proteins: Help maintain muscle mass and support metabolism.
- Fats: Provide sustained energy and prevent hunger.
Best Sources:
- Proteins: Chicken, turkey, lentils, and chickpeas.
- Fats: Nuts, seeds, and healthy oils like olive and coconut oil.
Practical Tips for Starting a Low Carb Diabetes Diet
- Plan Ahead: Prepare meals and snacks to avoid high-carb temptations.
- Monitor Blood Sugar: Check your levels regularly to understand how your body responds to the diet.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Work with experts at Deepa Hospital to tailor your plan.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By adopting a Low Carb Diabetes Diet, individuals can stabilize blood sugar, reduce complications, and improve overall well-being. At Deepa Hospital, we’re dedicated to providing personalized care and expert advice tailored to each patient’s needs. Let us help you take charge of your diabetes management journey with confidence and clarity.

