Knee replacement in young patients is becoming more common as advancements in medical technology have made it possible for people of various ages to undergo knee surgery. Traditionally, knee replacements were considered a solution for older adults. However, with increasing numbers of younger, active individuals experiencing knee pain due to injuries, arthritis, or other conditions, knee replacement at a young age is now an option.
This article will discuss knee replacement in young patients, its benefits, risks, and how to prepare for the surgery. Whether you’re dealing with severe knee pain or considering your options, understanding knee replacement in young patients can help you make informed decisions about your health and future.
Benefits of Knee Replacement for Young Patients
Knee replacement in young patients offers several key benefits:
- Pain Relief: One of the most significant advantages is the relief from chronic knee pain, which allows patients to resume daily activities.
- Improved Mobility: Knee replacement at a young age can help restore mobility, making it easier to move, walk, and engage in sports or exercise.
- Long-Term Quality of Life: With proper rehabilitation, young patients can enjoy a better quality of life, free from constant pain.
- Durability: With advances in materials and surgical techniques, knee replacements are lasting longer, making it an ideal option for younger patients.
- Increased Independence: Many younger patients find that knee replacement gives them the freedom to live independently without being hindered by knee pain.
Risk of Knee Replacement for Young Patients
While knee replacement in young patients has its benefits, there are also risks involved:
- Implant Wear and Tear: Total knee replacement in young active patients may result in the premature wear of the prosthetic, as younger individuals tend to be more active, which can shorten the lifespan of the implant.
- Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection at the surgical site.
- Blood Clots: There is also the possibility of developing blood clots after knee surgery.
- Rehabilitation Time: Young patients may face a longer recovery period due to the complexity of the surgery.
- Need for Revision Surgery: In some cases, younger patients may require revision surgery later in life if the knee replacement wears out or fails prematurely.
How Young Is Too Young for Knee Replacement?
The youngest age for knee replacement surgery is not set in stone and depends on several factors, including the patient’s overall health and the severity of their knee condition. However, most doctors recommend that knee replacement in young patients be considered only after all other options have been exhausted.
The youngest age for knee replacement surgery is typically around 50, although in some cases, patients as young as 40 may undergo surgery. Younger individuals often require a more customized treatment plan, as their active lifestyle may impact the longevity of the knee implant. The decision to move forward with surgery should be made after careful consultation with an orthopedic surgeon.
How to Prepare for Knee Replacement?
Preparing for knee replacement in young patients involves a few critical steps:
- Medical Evaluation: Your doctor will perform a thorough examination to ensure that you are a good candidate for knee replacement surgery.
- Physical Therapy: Some doctors recommend pre-surgery physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Patients may be asked to stop certain activities, such as smoking, which can affect healing, and to improve their diet for better overall health.
- Post-Surgery Planning: It’s important to plan for post-surgery rehabilitation. Arrange for help at home, as mobility will be limited initially.
- Understand the Procedure: Make sure you fully understand the surgical process, risks, and benefits.
Can Younger People Get Knee Replacements?
Yes, younger people can get knee replacements, and the procedure is becoming more common among individuals under 50. Knee replacement in young patients is usually considered when other treatments, like physical therapy or medication, no longer provide relief from knee pain. Total knee replacement in young active patients is often necessary due to severe knee injuries or conditions like osteoarthritis, which can affect individuals in their 40s and 50s.
However, since younger patients are more likely to be physically active, their knee replacements may wear out more quickly than those of older patients. It’s important to consider the long-term implications and work with a skilled orthopedic surgeon to choose the best knee replacement for young active patients.
Replacement Results in Young Patients
Knee replacement in young patients generally has good results, but it is essential to manage expectations. Many young patients experience a significant reduction in knee pain and an improvement in mobility. They can return to normal activities such as walking, climbing stairs, and even participating in low-impact sports. However, young active individuals may experience issues with the longevity of their implants.
As the prosthetic joint wears down over time, some patients may need revision surgery earlier than older patients. To ensure the best results, it is crucial to follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding rehabilitation and lifestyle adjustments.
Conditions Knee Replacement Required in Younger Patients
Knee replacement in young patients is usually recommended for conditions that significantly impact the knee’s function. Some common conditions that might require knee replacement surgery in younger individuals include:
- Osteoarthritis: This degenerative joint disease is common in older adults but can affect younger patients, especially those with a family history or those who have experienced previous knee injuries.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: This autoimmune condition can cause severe inflammation in the knee, leading to pain and loss of function.
- Knee Deformities: Conditions like knee dysplasia or a history of joint instability may lead to the need for knee replacement.
- Injuries: Severe knee injuries, such as fractures or ligament tears, may necessitate knee replacement when other treatments fail.
What to Avoid After Knee Replacement?
After knee replacement in young patients, there are several activities to avoid in order to ensure the best recovery and prevent complications:
- High-Impact Activities: Running, jumping, and activities that put too much pressure on the knee should be avoided.
- Twisting Movements: Sudden twisting or turning movements can strain the knee joint and potentially damage the prosthetic.
- Heavy Lifting: Lifting heavy weights can strain the knee and affect its stability.
- Overuse: It is essential not to overexert the knee too soon after surgery. Gradual rehabilitation is key to long-term success.
Understanding Knee Replacement and its Variations
Knee replacement surgery is a medical procedure designed to alleviate pain and restore function in individuals suffering from knee joint problems, often caused by arthritis, injury, or degenerative diseases. The surgery involves replacing the damaged parts of the knee with prosthetic components, generally made from metal, plastic, or ceramic materials. However, there are different variations depending on the patient’s condition, age, and activity level.
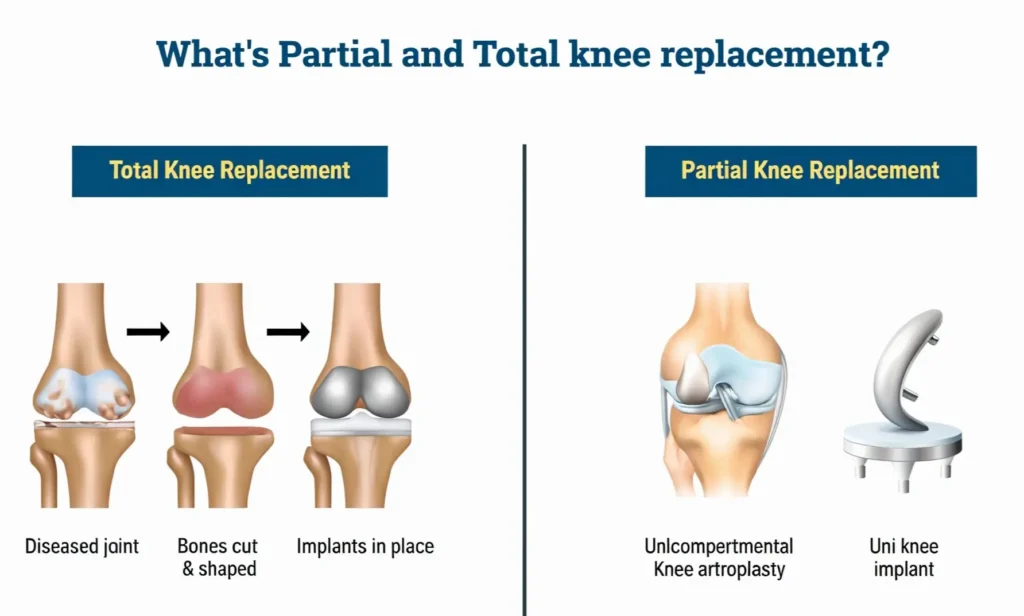
Types of Knee Replacement:
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR): Involves replacing the entire knee joint, often recommended for severe arthritis.
- Partial Knee Replacement: A less invasive option, replacing only the damaged portion of the knee joint.
- Knee Resurfacing: Involves only resurfacing the damaged areas of the knee rather than replacing it completely.
Total Knee Replacement in Young Active Patients:
In younger, more active patients, the decision to proceed with knee replacement is more complex. Though traditionally considered for older individuals, advancements in prosthetics and surgical techniques allow for better outcomes in younger patients.
The youngest age for knee replacement surgery varies, but it is generally considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief.
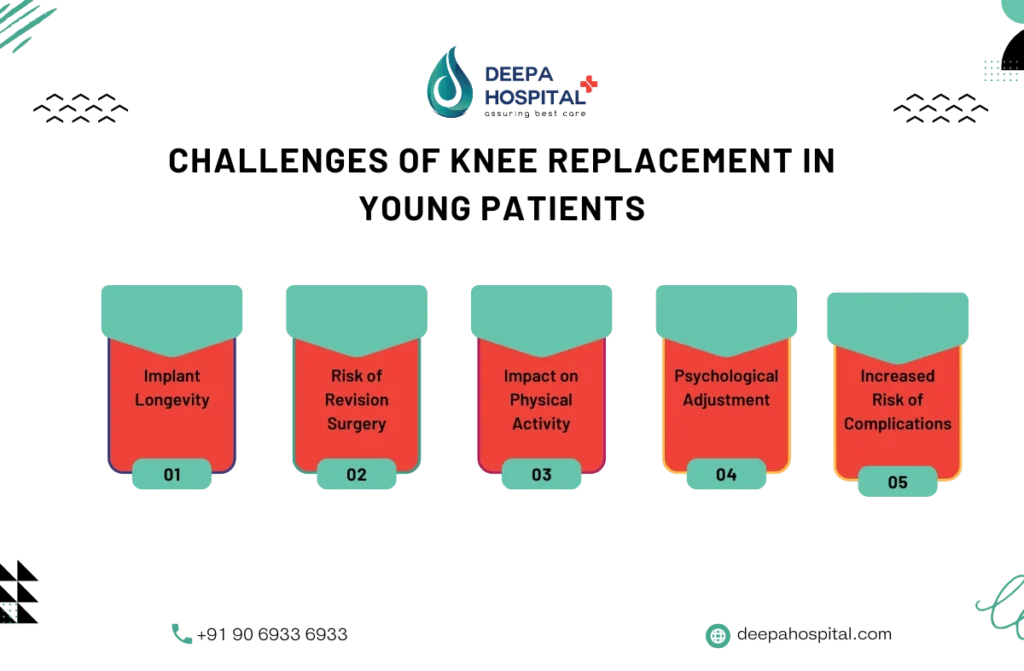
Challenges and Considerations in Younger Patients
Undergoing total knee replacement in young active patients presents unique challenges and considerations. While the procedure can restore mobility, younger individuals must consider long-term implications.
- Durability of Implants – Knee implants last around 15–20 years, requiring possible revision surgery in the future.
- Higher Activity Levels – Younger patients are more active, increasing implant wear over time.
- Post-Surgery Lifestyle Adjustments – High-impact activities may need to be limited to prolong implant life.
- Longer Recovery Period – Younger patients may expect a longer and more demanding rehabilitation process.
- Emotional and Psychological Impact – The need for knee replacement at a young age may impact mental well-being.
Despite the challenges, total knee replacement in young active patients can significantly improve quality of life when managed with proper medical guidance and rehabilitation.
Navigating the Path to Knee Surgery
Navigating the path to knee surgery involves a multi-step process aimed at ensuring the best possible outcomes for the patient. The journey begins with a thorough evaluation of the knee’s condition, followed by discussions on treatment options, and ultimately, surgical intervention if necessary.
Step 1: Initial Assessment and Diagnosis
A doctor will perform a detailed examination and may order imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs to assess the extent of the damage. The decision to recommend knee surgery depends on factors such as pain severity, loss of mobility, and the patient’s overall health.
Step 2: Exploring Non-Surgical Options
Before opting for surgery, doctors typically explore non-surgical treatments, such as physical therapy, corticosteroid injections, or hyaluronic acid injections, to manage pain and improve function.
Step 3: Surgical Decision
When non-surgical methods fail, knee replacement may be the most effective solution. The total knee replacement in young active patients is often a topic of discussion, as these patients may have higher expectations for long-term joint function.
Step 4: Post-Operative Recovery
After surgery, rehabilitation and physical therapy are critical to achieving a successful recovery. Early movement and strength-building exercises can ensure a smoother recovery and enhance the function of the new knee joint.
Choosing the youngest age for knee replacement surgery depends on individual circumstances, but it’s essential to weigh the risks and benefits carefully.
Conclusion
Knee replacement in young patients is a growing field, as more and more younger individuals are opting for surgery to address knee pain and improve their quality of life. While there are risks associated with knee replacement at a young age, the benefits often outweigh them for those who are dealing with severe knee pain or loss of function.
The best knee replacement for young active patients depends on several factors, including their age, lifestyle, and the severity of their condition. By carefully considering all options and working with a qualified orthopedic hospital, younger patients can enjoy a more active and pain-free life following knee replacement surgery.

