Is human metapneumovirus dangerous? This is a question many people are asking, especially with increased attention on respiratory illnesses in recent years. At Deepa Hospitals, we understand the concerns surrounding human metapneumovirus (HMPV) and are here to provide clear answers and guidance. Respiratory infections can be unsettling, but understanding the facts can help reduce fear and promote better health decisions.
What is Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a common respiratory virus that belongs to the same family as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). It primarily affects the lungs and airways, causing symptoms that range from mild to severe. HMPV is most common during the winter and early spring months and can infect individuals of all ages, though it poses a higher risk to young children, older adults, and those with weakened immune systems.
Is Human Metapneumovirus Dangerous?
Is human metapneumovirus dangerous? The answer depends on the individual affected. For most healthy people, HMPV causes mild symptoms similar to a cold, such as a runny nose, cough, and slight fever. However, for high-risk groups, such as the elderly or individuals with preexisting conditions, it can lead to severe respiratory problems like pneumonia or bronchitis. Early detection and treatment can significantly reduce complications.
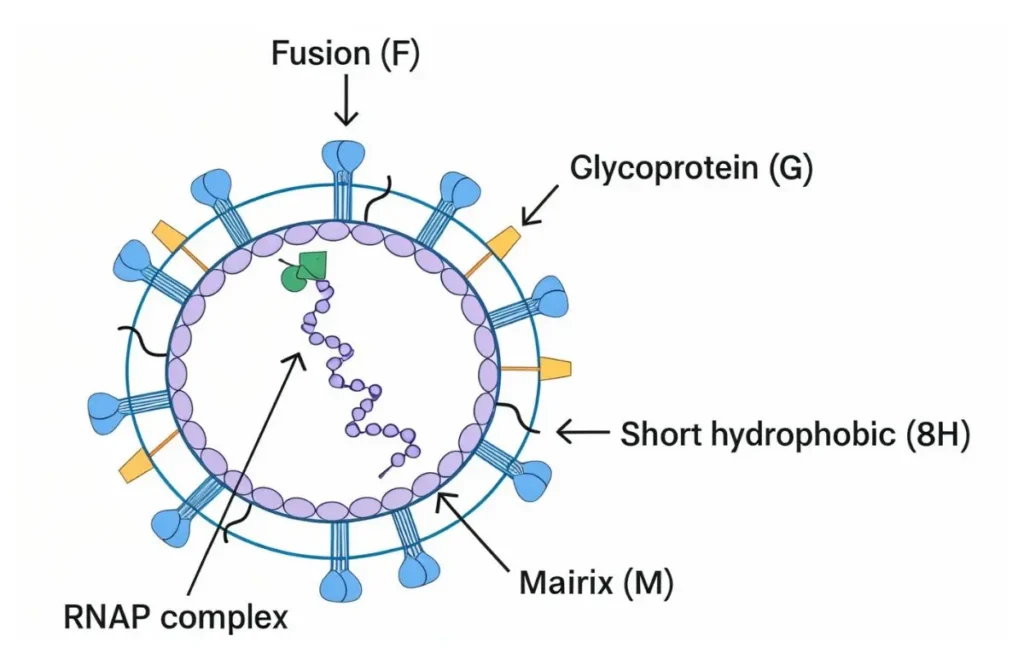
Is Human Metapneumovirus Just a Cold?
HMPV is often mistaken for a common cold because of its mild symptoms in healthy individuals. However, is human metapneumovirus dangerous? Yes, it can be in certain cases. Unlike a simple cold, HMPV can progress to more severe illnesses, especially in those with compromised health. If symptoms persist or worsen, it’s important to seek medical advice promptly.
Is HMPV as Dangerous as COVID-19?
Is HMPV as dangerous as COVID-19? No, HMPV is generally less severe than COVID-19. While both viruses can cause respiratory symptoms, COVID-19 has a higher potential for severe complications, including multi-system failure. That said, HMPV shouldn’t be ignored, as it can lead to hospitalization in vulnerable individuals. Comparing the two, it’s clear that both require attention and proper care to avoid serious outcomes.
Is Human Metapneumovirus Bad for You?
Is human metapneumovirus bad for you? For most individuals, HMPV is not a serious threat. However, it can be bad for individuals with underlying conditions or weakened immune systems. These groups are at higher risk of developing severe complications such as pneumonia. It’s important to monitor symptoms and seek medical attention if they worsen.
How Common is Human Metapneumovirus?
HMPV is more common than many people realize. It’s estimated that most people will have been infected with the virus by the age of five. Seasonal outbreaks occur annually, much like influenza. Is human metapneumovirus dangerous? While it’s common, it can become serious for vulnerable individuals.
Is Human Metapneumovirus the Same as COVID-19?
Is human metapneumovirus dangerous? While HMPV and COVID-19 share some overlapping symptoms, they are caused by different viruses. COVID-19 is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus and has more widespread and severe impacts, including long-term complications. HMPV, while serious in some cases, typically resolves without long-term effects for healthy individuals.
HMPV Dangerous or Not?
When assessing HMPV dangerous or not, it’s crucial to consider the individual’s health. For most, HMPV is not life-threatening. However, those with weakened immune systems or underlying conditions may experience severe symptoms, including difficulty breathing or lung infections. Preventive care and early intervention are key to managing this virus effectively.
HMPV vs. COVID-19
Understanding the differences between HMPV and COVID-19 can help alleviate confusion.
- Transmission: Both viruses spread through respiratory droplets. However, COVID-19 is more contagious and has a broader range of symptoms.
- Severity: Is HMPV as dangerous as COVID-19? No, but it can still cause serious illness in at-risk populations.
- Prevention: Hand hygiene, mask-wearing, and avoiding crowded places are effective in preventing both infections.
What Are the Symptoms of Human Metapneumovirus?
The symptoms of HMPV are similar to other respiratory infections. They include:
- Mild Symptoms: Runny nose, cough, sore throat, and low-grade fever.
- Severe Symptoms: Difficulty breathing, wheezing, and chest pain, particularly in high-risk individuals.
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, especially if they worsen, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. Is human metapneumovirus bad for you? Yes, in severe cases, which is why timely care is crucial.
What Causes a Human Metapneumovirus Infection?
HMPV is transmitted through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. You can also contract the virus by touching contaminated surfaces and then touching your face. Factors like close contact with infected individuals and poor hygiene practices increase the risk of infection. Preventive measures like handwashing and disinfecting commonly touched surfaces can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
What Are the Risk Factors for Human Metapneumovirus?
Certain groups are more vulnerable to severe HMPV infections, including:
- Young Children: Their developing immune systems make them more susceptible.
- Older Adults: Age-related immune decline increases risk.
- Individuals with Chronic Conditions: Asthma, heart disease, and COPD patients are at higher risk.
- Immunocompromised Individuals: Cancer patients, organ transplant recipients, and those on immunosuppressive therapy.
Preventive Tips for Human Metapneumovirus
Prevention is better than cure. Follow these tips to reduce your risk of HMPV:
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Avoid close contact with people who are sick.
- Keep your home clean and disinfect high-touch surfaces regularly.
- Stay home when you’re unwell to prevent spreading the virus to others.
- Vaccinations for other respiratory illnesses like influenza can also help protect against co-infections.
Conclusion
Is human metapneumovirus dangerous? While it’s usually mild, it can pose significant risks to vulnerable populations. Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and preventive measures is essential for protecting yourself and your loved ones.

