Pregnancy brings joy, but it also places unique demands on a woman’s body, including the liver. Fatty Liver While Pregnant, a condition where fat builds up in liver cells, can occur unexpectedly. This rare issue, linked with an enlarged liver during pregnancy and, in some cases, inflamed liver symptoms, needs prompt care. Supporting liver health during pregnancy is crucial for both the mother and baby. Early recognition and treatment can reduce risks and ensure a safer pregnancy journey.
What is Acute Fatty Liver While Pregnant?
Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy (AFLP) is a rare but life-threatening condition where fat accumulates excessively in liver cells. It occurs late in pregnancy, usually in the third trimester. This condition can affect liver function, requiring immediate attention and liver support during pregnancy to ensure safety for the mother and child. Prompt diagnosis and management are essential to avoid complications.
How Common is Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy?
AFLP is rare, occurring in about 1 in 7,000 to 1 in 20,000 pregnancies. Though uncommon, it is crucial to stay vigilant about symptoms like nausea, jaundice, and abdominal pain. Early detection can save lives. Fatty Liver While Pregnant highlights the importance of liver support during pregnancy and understanding its warning signs.
Symptoms and Causes
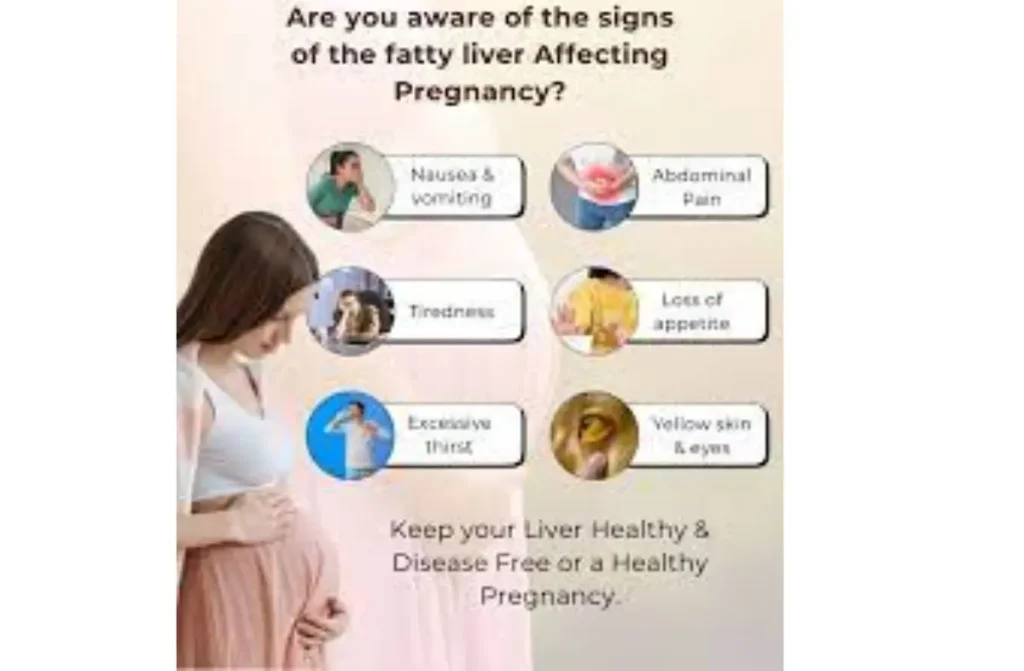
Symptoms of AFLP can develop quickly. Look out for:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain, especially in the upper-right area
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Fatigue or confusion
- Excessive thirst and increased urination
Recognizing these symptoms early is key to managing Fatty Liver While Pregnant. Liver support during pregnancy can help prevent severe outcomes.
What is the Cause of Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy?
The exact cause isn’t fully understood, but genetic factors and abnormal fat metabolism in the liver are major contributors. A deficiency in enzymes that process fatty acids can trigger this condition. Ensuring liver health and support during pregnancy can reduce risks.
7 Proven Ways to Manage Fatty Liver While Pregnant
| Strategy | Details |
|---|---|
| Balanced Diet | Incorporate whole grains, lean proteins, and vegetables. Limit fatty and sugary foods to prevent fat accumulation in the liver. |
| Regular Exercise | Engage in safe pregnancy exercises like walking or yoga to maintain a healthy weight and improve liver function. |
| Hydration | Drink plenty of water to support liver detoxification and reduce inflammation. |
| Frequent Health Checkups | Regularly monitor liver function with your doctor, especially if dealing with an enlarged or inflamed liver during pregnancy. |
| Avoid Alcohol | Completely eliminate alcohol to prevent further fat accumulation and liver damage. |
| Controlled Weight Gain | Gain weight gradually and within recommended guidelines to avoid excessive strain on the liver. |
| Medications Under Guidance | Only take prescribed medications for any existing conditions to avoid negative impacts on the liver. |
Risk Factors of AFLP (Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy)
Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy (AFLP) is a rare but serious condition that affects pregnant women, usually in the third trimester. Certain factors can increase the risk of developing AFLP, leading to severe complications if left untreated.
Common Risk Factors:
- Genetic Predisposition – Women with a history of metabolic disorders may be more susceptible.
- Multiple Pregnancies – Carrying twins or more increases the chances of developing AFLP.
- Obesity and Poor Diet – Excess weight and an unhealthy diet may contribute to an inflamed liver during pregnancy.
- Pre-existing Liver Conditions – Women with liver disease or hepatitis have a higher risk.
- Fetal Genetic Disorders – Some genetic mutations in the baby can trigger AFLP.
Recognizing these risk factors early can help prevent severe complications and ensure better maternal and fetal outcomes.
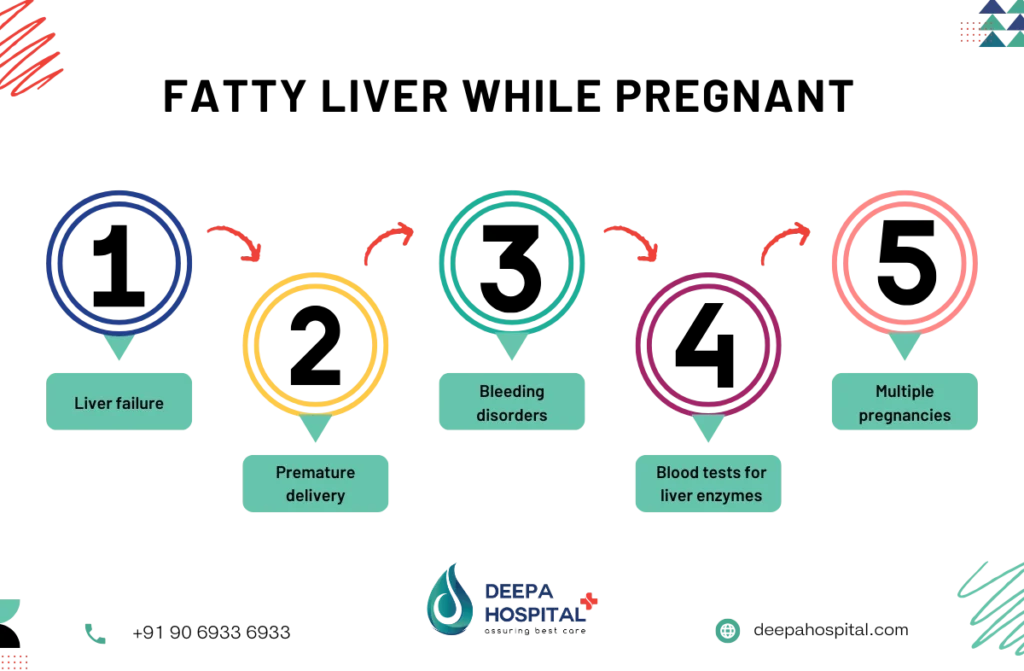
Complications of AFLP
If not diagnosed and treated promptly, AFLP can lead to life-threatening complications for both the mother and baby. The liver struggles to process fats, leading to widespread issues affecting multiple organs.
Potential Complications:
- Liver Failure – Severe cases can result in complete liver dysfunction.
- Kidney Dysfunction – AFLP may lead to acute kidney injury.
- Coagulation Disorders – The blood’s ability to clot is impaired, increasing bleeding risks.
- Inflamed Liver During Pregnancy – Persistent inflammation can cause long-term liver damage.
- Preterm Birth – AFLP often leads to emergency deliveries to protect both mother and baby.
Early diagnosis and medical intervention are crucial in managing AFLP and preventing serious health risks.Pregnant needs urgent care to avoid these risks. Liver support during pregnancy ensures better outcomes.
Treatment for Fatty Liver
Fatty liver disease is manageable with timely intervention and lifestyle modifications. Treatments focus on addressing the underlying causes and preventing progression to severe liver damage. Key recommendations include:
- Adopting a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can reduce fat buildup in the liver.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in moderate physical activity for at least 30 minutes daily improves liver health.
- Weight Management: Losing 5-10% of body weight can significantly reduce fat in the liver.
- Medication: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage related conditions like diabetes or high cholesterol.
For pregnant individuals, monitoring is essential as conditions like an enlarged liver during pregnancy may complicate management. Regular follow-ups with a hepatologist ensure the disease is under control and reduces the risk of complications.
Diseases & Conditions Related to Fatty Liver
Fatty Liver While Pregnant can lead to several complications if left untreated, including:
- Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): A severe form of fatty liver with inflammation and liver cell damage.
- Liver Fibrosis: Scarring of liver tissue due to chronic inflammation.
- Cirrhosis: Advanced liver scarring that may lead to liver failure.
- Liver Cancer: Long-term fatty liver disease increases the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Pregnancy-related conditions like an inflamed liver during pregnancy can exacerbate fatty liver disease, requiring specialized care. Early detection and tailored treatments prevent these conditions from progressing and ensure better liver health.
Prevention
While AFLP cannot always be prevented, you can reduce risks by:
- Regular prenatal checkups
- Monitoring liver health
- Staying informed about symptoms
Supporting your liver during pregnancy ensures a healthier experience.
Outlook / Prognosis
With timely care, most women recover fully. The liver usually returns to normal function after delivery. Keeping an eye on symptoms and focusing on liver health during pregnancy helps avoid long-term effects.
Conclusion
Fatty Liver While Pregnant is a rare condition but manageable with the right care. Recognizing symptoms like an enlarged or inflamed liver during pregnancy and seeking early treatment ensures the safety of both mother and baby. Regular prenatal visits and liver support during pregnancy are essential for a smooth journey. Stay proactive to enjoy a happy, healthy pregnancy.

