Living with diabetes can be challenging, but managing your diet is a key factor in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Creating the best diet plan for diabetics involves choosing foods that help regulate glucose levels while providing necessary nutrients. In this blog, we’ll explore the essential components of a healthy diabetic diet, explain why you need a personalized eating plan, and offer a 7-day diet chart for diabetic patients to help you from Diabetes.
Why Do You Need to Develop a Healthy-Eating Plan?
A healthy diet plan for high sugar patients is essential to control cholesterol, and weight. A well-structured plan ensures you’re getting balanced nutrition without spiking your blood sugar. The best diet plan for diabetics can reduce the risk of heart disease and other complications. For those with diabetes, maintaining a healthy diet isn’t just about avoiding sugar; it involves choosing foods that provide energy and stabilize glucose levels throughout the day.
Key Benefits of a Healthy Diet Plans for Diabetics:
- Helps manage blood sugar levels.
- Reduces risk of complications such as heart disease.
- Promotes healthy weight management.
- Provides balanced nutrition.
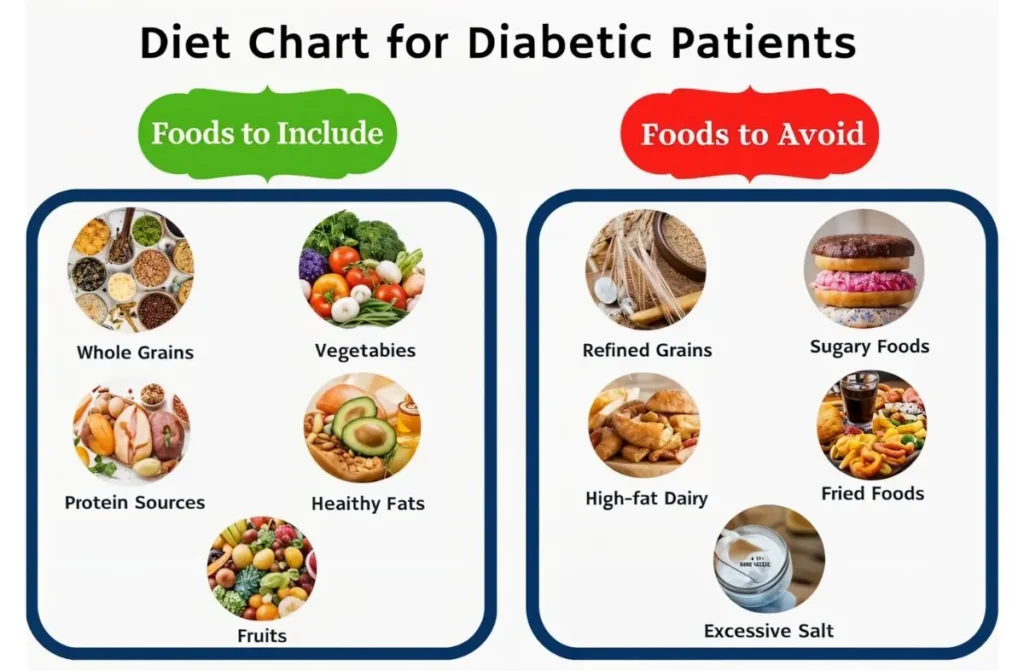
Recommended Foods for Diabetics
When planning the best diet plan for diabetics, it’s important to focus on nutrient-dense foods. These provide the body with energy and essential nutrients without spiking blood sugar.
Recommended food groups include:
- Whole grains
- Vegetables (especially leafy greens)
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats
Healthy Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates have the most direct impact on blood sugar, but not all carbs are bad. The best diet plan for diabetics should include healthy carbs like:
- Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, oats)
- Vegetables (non-starchy like spinach, kale)
- Fruits (in moderation)
- Legumes (beans, lentils)
Avoid simple sugars and refined carbs like white bread, sugary snacks, and sodas, which cause blood sugar spikes.
Fiber-Rich Foods
Fiber is an essential part of a healthy diet plans for diabetics because it helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes digestive health. High-fiber foods take longer to break down, slowing glucose absorption.
High-fiber foods include:
- Vegetables
- Whole grains
- Legumes
- Fruits (with the skin)
Adding fiber-rich foods can help reduce the need for insulin and other medications, making them an important part of the best diet plan for diabetics.
Heart-Healthy Fish
Fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon and mackerel, can lower the risk of heart disease, which is a common concern for people with diabetes. Including these in the best diet plan for diabetics supports heart health while providing high-quality protein.
Good Fish Choices:
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Herring
Good Fats
Not all fats are bad for you! The best diet plan for diabetics includes healthy fats, which can improve heart health and help manage blood sugar.
Healthy fat sources include:
- Avocados
- Nuts (in moderation)
- Seeds
- Olive oil
Protein
Protein is an essential part of any healthy diet plans for diabetics. It doesn’t raise blood sugar levels and helps you feel full, which can prevent overeating.
Good Protein Sources:
- Lean meats (chicken, turkey)
- Fish
- Eggs
- Plant-based proteins (tofu, legumes)
7-Day Diet Chart for Diabetic Patients
Here’s a detailed 7-Day Diet Chart for Diabetic Patients in a table format. This diet plan for high sugar patients focuses on balanced nutrition, portion control, and managing blood sugar levels while including healthy carbohydrates, lean proteins, and good fats.
| Day | Breakfast | Mid-Morning Snack | Lunch | Afternoon Snack | Dinner | Bedtime Snack |
| Day 1 | Oatmeal with berries and chia seeds | A handful of almonds | Grilled chicken salad with olive oil dressing | 1 Apple or pear | Baked salmon with steamed broccoli and quinoa | A small cup of Greek yogurt |
| Day 2 | Whole grain toast with mashed avocado and poached eggs | A small bowl of cucumber slices | Lentil soup with a side of leafy greens salad | 1 small orange | Stir-fried vegetables with tofu and brown rice | A handful of mixed nuts |
| Day 3 | Greek yogurt with mixed berries and a sprinkle of flaxseeds | 1 boiled egg | Turkey lettuce wrap with hummus and raw veggies | A small serving of baby carrots | Grilled chicken breast with sautéed spinach and sweet potatoes | 1 small apple |
| Day 4 | Scrambled eggs with spinach and whole wheat toast | 1 serving of cottage cheese | Grilled fish (cod or tilapia) with a quinoa and kale salad | A few almonds or walnuts | Baked cod with roasted Brussels sprouts and carrots | 1 glass of unsweetened almond milk |
| Day 5 | Smoothie with spinach, almond milk, berries, and chia seeds | A small handful of walnuts | Vegetable stir-fry with tofu, served with brown rice | A small serving of mixed berries | Grilled shrimp with a mixed greens salad and olive oil dressing | A small cup of low-fat yogurt |
| Day 6 | Whole grain pancakes with a sprinkle of cinnamon and fresh strawberries | 1 small banana | Tuna salad with whole grain crackers and a side of cucumber slices | A handful of roasted chickpeas | Beef stir-fry with broccoli and carrots | A small handful of sunflower seeds |
| Day 7 | Scrambled eggs with mushrooms and a side of sliced avocado | 1 pear | Chicken and vegetable soup with a side of whole wheat bread | A small handful of mixed nuts | Grilled turkey burger (no bun) with sweet potato fries and a side salad | A small portion of cottage cheese |
Additional Information:
- Portion Control: Aim to have moderate portion sizes to avoid overeating and manage blood sugar effectively. Use a smaller plate if needed.
- Balanced Macronutrients: Each meal includes a healthy balance of carbohydrates, protein, and fats to keep blood sugar stable.
- Healthy Snacks: Mid-morning and afternoon snacks help maintain blood sugar levels between meals and avoid large spikes or dips.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Limit sugary drinks and alcohol.
- Customization: This diet chart can be modified based on your specific needs or food preferences. Consult a nutritionist for a personalized plan.
This 7-day diet chart for diabetic patients is designed to help you manage your diabetes care by providing nutrient-rich foods, fiber, and healthy fats to regulate blood sugar levels.
Why a Meal Plan is Important
A well-structured meal plan is essential for managing health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or high blood sugar. Below are some reasons why having a meal plan is important:
- Maintains blood sugar levels: A consistent meal plan helps prevent spikes and crashes in blood sugar, crucial for those following healthy diet plans for diabetics.
- Encourages balanced nutrition: A meal plan ensures you’re getting the right balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- Portion control: It helps manage portion sizes, which is key for maintaining or losing weight.
- Reduces stress: Planning meals ahead reduces the daily stress of deciding what to eat.
- Prevents unhealthy eating: A structured plan reduces the temptation to eat high-sugar or processed foods, vital for a diet plan for high sugar patients.
Having a diet plan for high sugar patients is crucial in maintaining overall well-being and preventing complications.
What Are the Causes of Diabetes?
Diabetes occurs when the body is unable to properly regulate blood sugar levels, often due to insufficient insulin production or resistance to insulin. The primary causes include:
- Genetics: A family history of diabetes increases the risk.
- Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, can lead to insulin resistance.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to poor glucose management.
- Dietary Choices: High intake of sugary, processed foods can strain the body’s ability to manage blood sugar.
- Hormonal Disorders: Conditions like PCOS or Cushing’s syndrome may contribute.
Understanding the causes is key to managing diabetes effectively. Pairing lifestyle changes with a 7-day diet chart for diabetic patients and consulting experts can prevent or delay complications.
Nutrition and Diabetes
Proper nutrition plays a critical role in managing diabetes and maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Following the best diet plan for diabetics can help in:
- Controlling Blood Sugar: Balanced meals with low-glycemic index foods prevent spikes.
- Promoting Weight Loss: A tailored plan helps reduce body fat, improving insulin sensitivity.
- Boosting Energy: Nutrient-dense foods sustain energy throughout the day.
A 7-day diet chart for diabetic patients typically includes:
- Whole grains like brown rice and quinoa.
- Lean proteins such as chicken or legumes.
- Healthy fats from nuts, seeds, and avocados.
- Fiber-rich vegetables and limited fruits.
The best diet plan for diabetics ensures meals are portion-controlled and spaced out to maintain glucose balance, contributing to overall well-being.
Foods to Avoid for Diabetics
To maintain the best diet plan for diabetics, it’s important to avoid foods that spike blood sugar or add unhealthy fats to your diet. Some foods to steer clear of include:
- Sugary snacks (cookies, cakes)
- Sweetened beverages (sodas, sweet tea)
- White bread and pasta
- Fried foods
- Processed snacks (chips, candy)
Avoiding these foods will help you stick to your healthy diet plan for pre diabetics and keep your blood sugar under control.
Are There Any Risks?
While following the healthy diet plan for pre diabetics, it is crucial to be aware of potential risks:
- Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia): Avoid skipping meals to prevent sudden sugar drops.
- Nutrient Deficiency: Ensure a balanced intake of vitamins and minerals.
- Digestive Issues: Too much fiber can cause bloating; balance is key.
- Over-Reliance on Artificial Sweeteners: Some sweeteners may impact gut health and insulin sensitivity.

Conclusion
Developing the best diet plan for diabetics is essential to maintaining stable blood sugar and preventing complications like heart disease. By choosing nutrient-dense foods such as whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, you can manage your diabetes more effectively. Follow the 7-day diet chart for diabetic patients as a guide to get started. Remember, sticking to a balanced diet and avoiding processed foods is key to managing your health.
For more information or personalized diet plans, feel free to contact our best Endocrinologist. Take control of your health today.
Read Also: Can Honey Cause Diabetes

